EBUS Guided Mediastinal Lymph Node Biopsy
An EBUS-guided mediastinal lymph node biopsy is a minimally invasive procedure used to obtain tissue samples from lymph nodes located in the mediastinum (the area between the lungs). It is performed using a special bronchoscope equipped with an ultrasound probe—called an endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) scope.
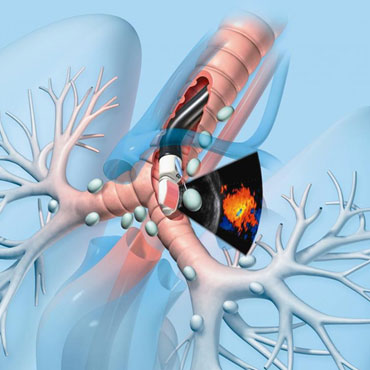
What is EBUS TBNA?
Endobronchial ultrasound Transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) is a reliable and an established technique, which can be perceived as the current gold standard that enables visualisation and sampling of Mediastinal or hilar lymph nodes under real time ultrasound guidance.
Purpose:
- To diagnose or stage lung cancer
- To diagnose causes of Lymph node enlargement in different cancers
- To detect infections, lymphoma, sarcoidosis, or tuberculosis
- To diagnose Sarcoidosis and infections like tuberculosis
How is EBUS TBNA performed?
EBUS TBNA procedure is most often performed under local anesthesia and sedation on day care basis. Sometimes patients may need to be hospitalised. The dedicated EBUS TBNA bronchoscope is passed orally through the vocal cords into the airway. The Mediastinal and hilar lymph nodes are visualised on the monitors using the ultrasound probe at the tip of bronchoscope. The EBUS-TBNA needle is inserted into the lymph nodes under real time ultra sound guidance and samples obtained.
What are the Chances of Making the Diagnosis?
The diagnosis yield on EBUS-TBNA may vary from 74% to 95%.
Advantages:
- Less invasive than surgical biopsy
- Performed under conscious sedation or general anesthesia
- Quick recovery and low risk of complications
Why It’s Important:
This procedure provides accurate diagnosis and staging, especially in lung cancer, without the need for more invasive surgery like mediastinoscopy.